Large Capacity ASME Code Filter Vessels
Large Capacity ASME Code Filters
Finite's filter vessels eliminate oil, water, and particulate contamination from large flows of compressed air and gas.
Finite Filter’s large capacity ASME filter vessels have been designed specifi cally for our coalescing elements and incorporate large sump capacities and generous exit cavities for maximum performance with low differential pressures.
All units are “U” stamped and conform to ASME Section VIII standard code for pressure vessels. With flow capacities to 37,000 SCFM and optional materials of construction, most compressor source filtration requirements can be met.
Standard Specifications
- Porting to: 16″ Flange
- Flows to: 37,000 SCFM (63,000 m3/hr)
- Design: ASME Code/CRN (Canadian Registration)
- Max. Temp: 450°F
- Max. Pressure: 185 PSIG
- Filter Media: Coalescing, Particulate, Vapor Adsorption, and Bulk Liquid Removal
- Confi guration: Floor-Standing or Line-Mounted
- Drain and Vent Ports: ½” NPT
- Design allows for easy element changeout
Typical Applications
Coalescing (Oil Removal)
- Compressed air system protection
- Dryer protection – Mist eliminator
- Paint spray booths
- Microelectronics quality air prefiltration
- Landfill gas
- Natural gas treatment
Interceptor (Particulate Removal)
- Natural gas inlet systems
- Desiccant dryer afterfilter
- Prefi lter for coalescer
- Systems with high particulate concentration
- Particulate protection for non-lubricated systems
Adsorber (Vapor Removal)
- Odor removal
- Food packaging
- Powder paint systems
- Blow molding
- Breathing air
Custom options include:
- Stainless steel vessels (304 & 316 SS options)
- High pressure
- Corrosion allowance
- Non-standard port orientation
- Sight glass ports
- Custom name plates
- Liquid level control connections
- P.E.D. Compliant
Compressed Air Standards and Applications
ISO 8573-1 is an international standard that has become the universally accepted method for specifying and testing the purity of compressed air. ISO 8573-1 specifies a purity “class” based on contaminants in compressed air.
There are three classes that describe 1) particulate contamination concentration, 2) liquid or vaporous water contamination concentration, and 3) the contamination concentration caused by oil in the liquid, aerosol, and vapor states.
The ISO purity class is always stated using three numbers in a definite order: the solid particulate class, followed by the water contamination class, and finally the oil contamination class. Use the table below to see how the purity classes for each contaminant type are defined.
Notification as specified in ISO 8573-1
Class | Solid | Water | Oil | ||||
Maximum Particle Size | Maximum Concentration | Maximum Pressure Dew point | Maximum Concentration | ||||
μm | ppm | (mg/m3) | oF | (oC) | ppm | (mg/m3) | |
1 | 0.1 | 0.08 | (0.1) | -94 | (-70) | 0.008 | (0.01) |
2 | 1 | 0.8 | (1) | -40 | (-40) | 0.08 | (0.1) |
3 | 5 | 4.2 | (5) | -4 | (-20) | 0.83 | (1) |
4 | 15 | 6.7 | (8) | 37 | (+3) | 4.2 | (5) |
5 | 40 | 8.3 | (10) | 45 | (+7) | 21 | (25) |
6 | – | – | – | 50 | (+10) | – | – |
Typical Applications
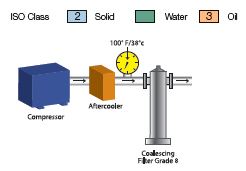
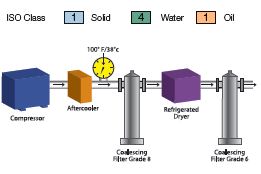
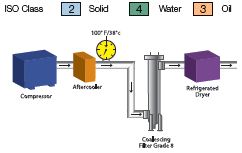
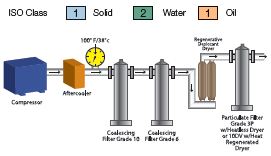
Note: In the pictorial examples shown above, the contribution of hydrocarbon vapors has not been taken into account in determining the oil class category.
